Information Flows & Data Journeys
Think of the main business processes running within your organisation. How many of us understand the complete journey that the data associated with that process will take and what the risks to that data could be? Understanding WHERE the data is at any given point in the process, WHAT format the data is in, HOW it is being used and WHO is accessing the data will go a long way to providing the answer to that question and also provide the basis of any required remedial action in order to be compliant with any relevant regulations, including GDPR/UK DPA 2017.
Let’s take a fairly standard call centre based sales process information flow, as shown in the example below:
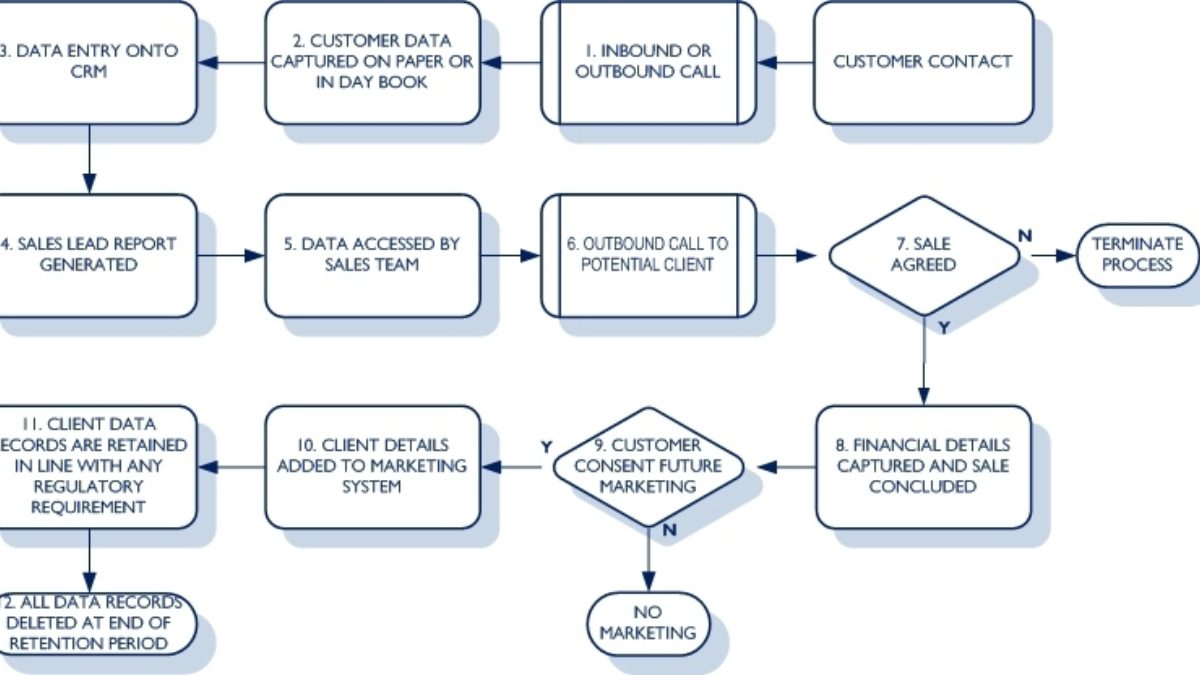
Each step of this process carries potential regulatory compliance, data protection or information security risks that, with the application of some simple common sense policies and (if required) some technology solutions, can be managed to help ensure that your organisation remains compliant with any government or industry regulations that may apply to you organisation.
Looking at the process points in more detail and using GDPR/UK DPA 2017 as a compliance target model, the table below shows how the high level compliance actions and data journey checkpoints relate to various process points:
1: Customer Contact
Compliance: Validate existing client data for accuracy and previous “Do Not Contact” notices on CRM system, prior to contact if outbound call. Seek consent from new clients to capture data and direct them to company privacy notices.
Data Journey: Is this data held anywhere else apart from the main CRM system? If so is it in sync?
2. Customer data capture on paper or in day book
Compliance: All relevant paper should be secured/disposed of in line with information security policy.
Data Journey: Is your organisation aware of the vulnerability of sensitive paper to theft, and how such paper should be treated with care prior to entry onto CRM system?
3. Data entry onto CRM system
Compliance: Potential client data should be accurate and should only be accessed by correct employees on “need to know” basis.
Data Journey: How do you currently avoid the creation of duplicate data sets across different storage media?
4: Sales lead generated
Compliance: Ensure that reports are generated from CRM system and are either correctly archived (i.e. traceable) or deleted after use.
Data Journey: Are sales lead reports deleted after use? Are they stored in multiple locations? Are they sent as email attachments?
5: Data accessed by sales team
Compliance: Data should only be used for the purpose intended and only by the correct staff on a “need to know” basis.
Data Journey: Are any notes made against the potential client stored on the CRM system? Are relevant emails being attached to the CRM system?
6: Outbound call to potential client
Compliance: The client should be informed if the call is being recorded and give their direct consent.
Data Journey: Are staff aware that voice recordings should be viewed as part of client data processing and that these will need to be traceable and recoverable against a Subject Access Request?
7: Sale agreed/not agreed
Compliance: If a new client does not agree to the sale then their consent should be sought at this point to maintain their records for future use. If not these should be deleted.
Data Journey: Do all staff understand the implications of the stricter consent rules under GDPR?
8: Financial details captured and sale concluded
Compliance: The addition of financial details to a client record raise the sensitivity of that data set and this should be recognised in the way the data is handled and the “need to know” rules are kept.
Data Journey: Is there an awareness that when financial details are added to a recorded it is important that these are redacted from any reports (except for financial teams)?
9: Customer consents/does not consent to future marketing
Compliance: If the client does not consent to future marketing contact, then a note should be added to their record and their details should not be added to any marketing systems.
Data Journey: Is there a defined method for dealing with “do not contact” requests?
10: Client details added to the marketing system
Compliance: If client consents to being added to marketing system then the same rules around consent, privacy and retention rules apply as for any CRM systems.
Data Journey: Is client data being held on the minimum number of systems and locations possible to meet the legitimate business interests of your organisation?
11: Client data records are retained in line with any regulatory requirements
Compliance: Client data records should be kept in line with any regulatory requirements and this will form the basis of the data retention period i.e. a VAT transaction must be kept for 7 years.
Data Journey: Does each business area have a retention policy detailing where data records are being held (i.e. CRM system, network drive, Sharepoint) and when “the clock” has started on each data record?
12: All data records deleted at the end of the required retention period
Compliance: All client data records should be deleted at the end of the correct retention period and proof of their deletion kept in case of later complaint.
Data Journey: Is there a process of proof of deletion as the final piece of the “data journey”?
This is a high level view of what is a usually an in-depth analytical process, but if you require any further information on the various services we provide in this field, please contact us:
Deborah Walker - Business Development Manager: 07774 914254
Alex Mann - Account Manager: 02380 606 154
